Windows environment variables are important in order to provide certain data or settings for programs at the operating system level. These Windows variables can either be user-defined or set as system variables . The only difference is that the assigned values and variables only apply to the logged-in user, whereas the system variables are set the same for all users of a PC.
These environment variables used to have a big impact on the system, especially in the first version of Windows. In the meantime, the use of these Windows variables is disappearing more and more. Nevertheless, we want to show you today how you can view and edit them.
Query variables with SET
The easiest way is to have all the variables used displayed. This works by entering the following command in the command prompt.
SET
The following display appears, which of course can vary greatly depending on the PC and system.
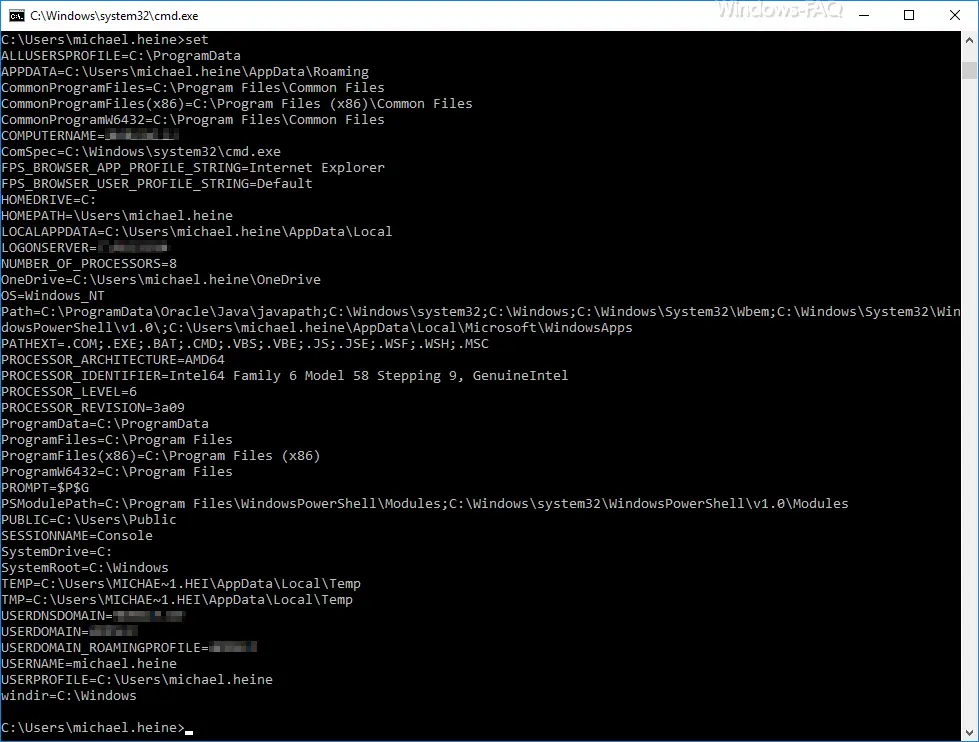
Each variable has a special meaning. Below we have given you a small overview of the most important Windows system variables .
- ALLUSER PROFILES
- APPDATA
- CommonProgramFiles
- CommonProgramFiles (x86)
- CommonProgramW6432
- COMPUTERNAME
- ComSpec
- FPS_BROWSER_APP_PROFILE_STRING
- FPS_BROWSER_USER_PROFILE_STRING
- HOMEDRIVE
- HOMEPATH
- LOCALAPPDATA
- LOGON SERVER
- NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS
- OneDrive
- OS
- Path
- PATHEXT
- PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE
- PROCESSOR_IDENTIFIER
- PROCESSOR_LEVEL
- PROCESSOR_REVISION
- ProgramData
- ProgramFiles
- ProgramFiles (x86)
- Program W6432
- PSModulePath
- PUBLIC
- SESSIONNAME
- SystemDrive
- SystemRoot
- TEMP
- TMP
- USERDNSDOMAIN
- USERDOMAIN
- USERDOMAIN_ROAMINGPROFILE
- USERNAME
- USER PROFILES
- WinDir
To edit these Windows variables, you have to press the key combination (Windows key + “R”)

call the program ” sysdm.cpl “. Then go to the ” Advanced ” tab and select ” Environment variables … ” below , as you can see below.
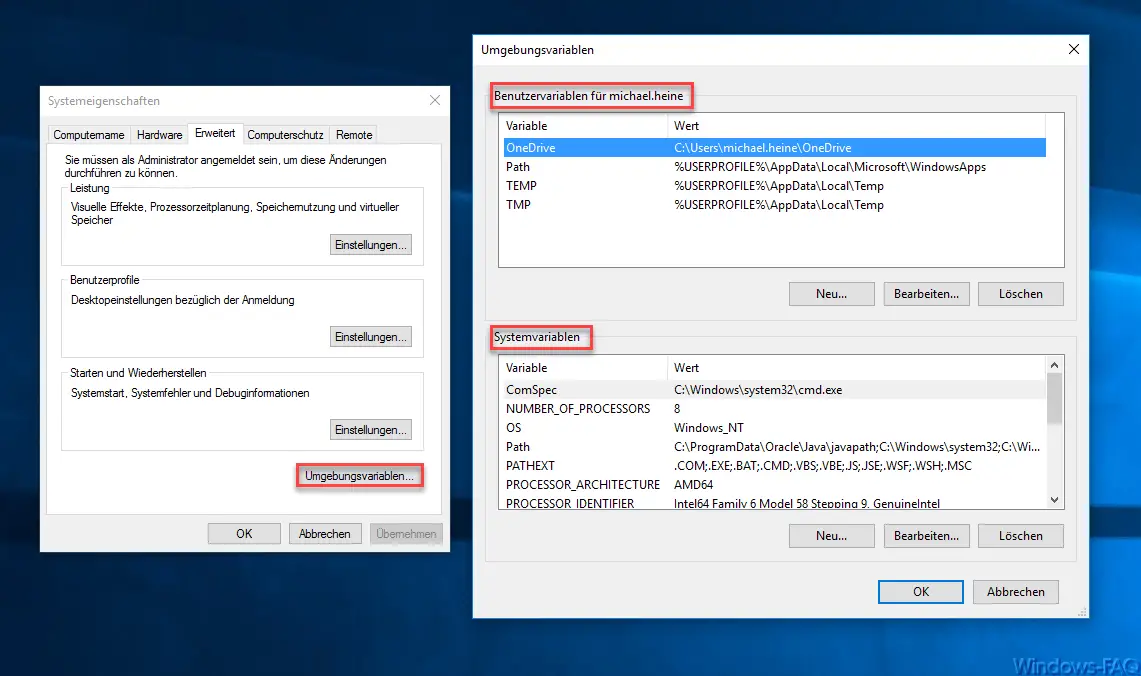
The window for editing the environment variables then opens . The editing area is divided into the groups ” User variables ” and ” System variables “. There you have the option to edit the existing variables, delete them and create new ones.
The changes take effect immediately, you can check this again very easily and quickly using the “set” command .
If you are interested in further interesting information about Windows , we recommend the following articles.
– Deactivate the Windows swap file
– Remove the on-screen keyboard symbol from the Windows 10 task bar
– Hide the desktop language bar (DEU) on the Windows 10 task bar
– Activate or deactivate the Chinese characters toolbar (MS-Pinyin IME)
– Activate or deactivate Windows 10 night mode
– Automatically rotate the screen / Disable monitor
display – AutoRotation – Show and delete Microsoft Edge browser history – Activate
time with seconds in Windows 10 Taskbar – Show
detailed status messages when Windows starts – Show
hidden files, folders and drives in Windows Explorer
– Do not show login names on the Windows logon screen
– WLAN Show password in plain text via DOS command
– Show UAC dialog on Windows 10 Desktop