
BITS to monitors or to check , is not so simple. In our yesterday article we already went into more detail on how to configure the BITS service (Intelligent Background Transmission Service) . How is it to be determined whether and how the service works at all.
The “BITSADMIN” command , which Microsoft also delivers with Windows 10 as standard, is used for this. BITS provides a variety of parameters and is already in version 3.0. BITSADMIN means ” BITS Administration Utility “. The following examples should generally be carried out in an MS-DOS command prompt with administrator rights.
The most important command to observe how BITS works and how it works is the command
BITSADMIN / monitor
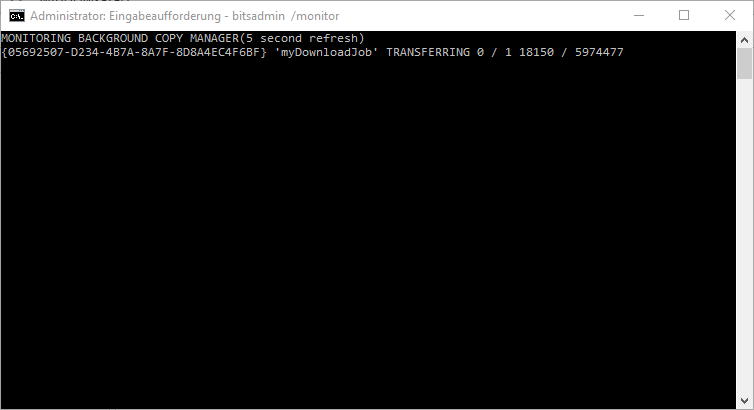
After entering the command, the BITSADMIN is called up in a special way and the display is automatically updated every 5 seconds until you end it with “CTRL” + “C” . In this way you can see live which requests are currently being processed by the BITS service .
Below you can already see a BITS activity , since we have started a manual download via the BITS service .
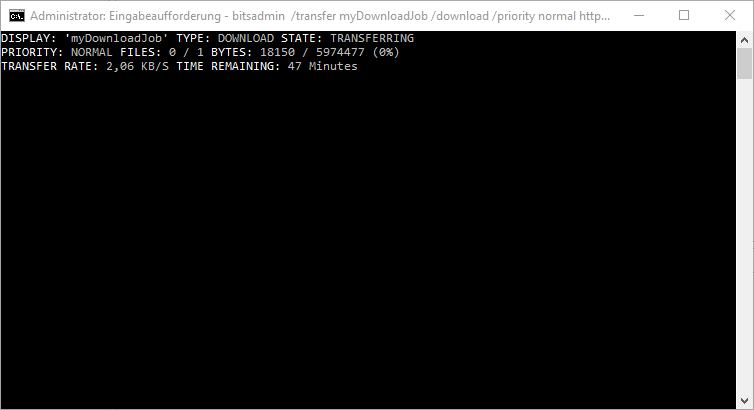
BITS can also be used for your own task, including the ability to download files from the Internet or your own network using the intelligent background transmission service . Here is an example of a download of a JPG image from the Windows FAQ homepage .
bitsadmin / transfer myDownloadJob / download / priority normal https://www.windows-faq.de/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/winter_wallpaper_8.png c: temp bild.jpg
With the parameter “/ transfer” you can determine the name of your download. You can then enter your download source in the name of the “priority” parameter , and the target file is then specified as the last parameter.
After issuing the command, you can see the download activity of the BITS service directly in the window in which you have issued the BITSADMIN Transfer command. At the same time , the download is also displayed in the window in which the BITSADMIN / Monitor is running.
Via the displayed ” Transfer Rate ” you can then check whether the download rate corresponds to the maximum speed that you have specified in the local group guidelines.
You can also use the ” Monitor ” parameter to monitor your Windows clients for Windows updates and their use. Especially when several Windows updates are called up in one process, numerous entries are displayed here.
If you are interested in other interesting commands related to Windows , take a look at the following articles.
– Shut down Windows 10 with the “SlideToShutDown” command
– Export AD groups to text files using a command
– Shutdown command and possible parameters
– Show the WLAN password in plain text using the DOS command
– Find out the Windows product
key using the DOS command or PowerShell – Rundll32 command – Parameters and explanations
– List Windows drivers using the Driverquery.exe
command – Quickly deactivate the Windows firewall